Writing scaffolder templates
Published on May 16th, 2022Overview
The Roadie Backstage scaffolder is a feature that allows you to define software templates to create new software projects, update existing ones or simply perform repeated tasks in a consistent manner.
Scaffolder templates are defined in YAML files and loaded into the Backstage catalog in the same way that other entities are loaded into Backstage. A template contains one or more steps which run sequentially during execution.
A Scaffolder template is then run on demand by the users of Backstage to execute the software template. Roadie will execute the software template in an ephemeral container that is destroyed after the execution completes.
You can find a step by step guide to adding templates in Roadie here
See the Backstage Scaffolder in action
Request a Roadie demoComponents of a Template
A Scaffolder template is a configurable process that will run one or more Scaffolder steps. The template will be run when a user visits the “Create Component” page in Backstage. https://<tenant-name>.roadie.so/create.
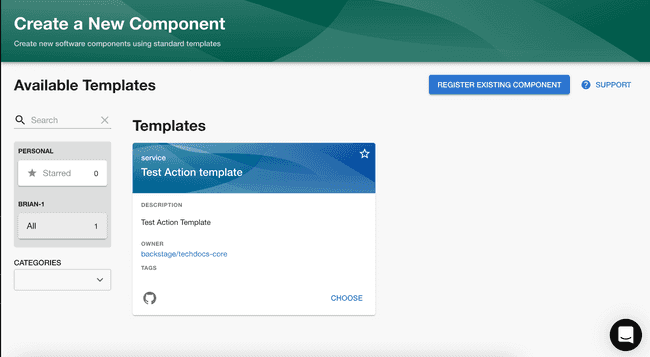
Templates are defined by a Backstage Entity YAML file with a Template kind and imported into the Backstage catalog. You can create multiple templates, each of which can perform a different set of steps. For example, you can have one template that creates a React application, and another that creates a serverless app.
Template YAML input forms can be tested at /tools using a live template preview viewer.
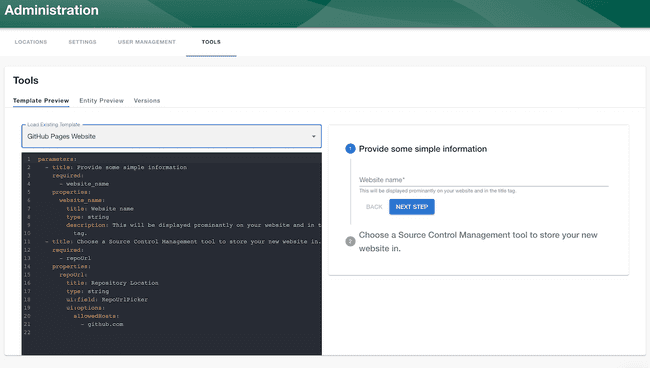
Here is an example of a very basic Scaffolder template that prompts the user for a name, and then prints back the text “Hello, name!”
apiVersion: scaffolder.backstage.io/v1beta3
kind: Template
metadata:
name: hello-world-template
title: Hello World
description: Says Hello to a specified name.
spec:
owner: backstage/techdocs-core
type: service
parameters:
- title: You are about to say hello to your first Backstage Template
required:
- name
properties:
name:
type: string
steps:
- id: log-message
name: Log Message
action: debug:log
input:
message: 'Hello, ${{ parameters.name }}!'Header Section
The header section is required for every template and contains information to configure the task and show details about the task on the “Create Component” page.
apiVersion: scaffolder.backstage.io/v1beta3
kind: Template
metadata:
name: hello-world-template
title: Hello World
description: Says Hello to a specified name.
spec:
owner: default/engineering
type: serviceapiVersion
This is a required field and should be set to scaffolder.backstage.io/v1beta3
kind
A Scaffolder template is also an Entity in Backstage. In order to configure this entity as a template you must set the kind to Template
metadata
The metadata field contains some data that appears on the template card that appears on the “Create Component” page.
spec
The spec field contains owner and type. Owner refers to the Backstage group or user that owns the Scaffolder task e.g. default/engineering. Type refers to the type of template. It can be set to anything and appears on the scaffolder template card in the “Create Component” page.
parameters
The parameters property is a list of parameters that can be prompted from the user when they run a template. Each array element contains the configuration for a single page of items to be filled by the user running the template. The parameter pages must contain title, required and properties.
The parameters yaml is based on react-jsonschema-form. You can find the available syntax options there and examples here.
You can choose to break up the parameter prompting into form steps or collect all the parameters in one single step.
Each parameter can be one of a few types: string, number, array or object.
Here is the most basic example:
parameters:
properties:
name:
type: stringValidation
You can use react-jsonschema-form to perform validation on input fields using a regex or character counts.
parameters:
properties:
name:
title: Simple text input
type: string
description: Description about input
maxLength: 8
pattern: '^([a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9]*)(-[a-zA-Z0-9]+)*$'
ui:autofocus: true
ui:help: 'Hint: additional description...'string
You may collect text data from the user by using the string type. Here is the most basic example. It will prompt the user for a name.
parameters:
properties:
name:
type: stringEntity picker
You can prompt the user with a list of catalog entities using the ui:field: EntityPicker option as follows:
parameters:
properties:
entity:
type: string
ui:field: EntityPickerOwned entity picker
Alternatively if you would like the user to only select entities that they already own, you might want to use the OwnedEntityPicker.
parameters:
properties:
ownedEntity:
type: string
ui:field: OwnedEntityPickerEntity name picker
If you would like a little validation when the user enters an Entity name, you can use the EntityNamePicker. It will prevent the user from entering an entity name that is not an acceptable entity name.
parameters:
properties:
ownedEntity:
type: string
ui:field: EntityNamePickerRepository picker
The respository picker can allow the user to select the name and location of a new repository. The picker restricts the target location of the repository to make it a little easier for the user to select a target location.
The following example, will only allow the user to enter a new repository name targeting the GitHub using the AcmeInc organization.
parameters:
properties:
repoUrl:
type: string
ui:field: RepoUrlPicker
ui:options:
allowedHosts:
- github.com
allowedOwners:
- AcmeIncThe RepoUrlPicker uses the allowedHosts to decide how to build the repo url output value. If you use bitbucket.org it will output a valid repo url for Bitbucket.
parameters:
properties:
repoUrl:
type: string
ui:field: RepoUrlPicker
ui:options:
allowedHosts:
- bitbucket.orgOwner picker
The owner picker, allows the user to select a user / group in the Backstage catalog. e.g.
parameters:
properties:
owner:
type: string
ui:field: OwnerPickerThis returns a variable in the format group:<namespace>/<group-or-user-name>. You can extract the entity name using replace when you refer to the parameter like so: ${{ parameters.owner | replace(\"group:.*/\", \"\") }}
Picker from external API source
This custom scaffolder field, makes an API call to the Backstage backend and allows the result to be rendered to a list.
parameters:
properties:
custom:
title: custom
type: string
description: Custom field from external API
# Use `SelectFieldFromApi` to configure the select field for the entry.
ui:field: SelectFieldFromApi
ui:options:
# The Path on the Backstage API and the parameters to fetch the data for the dropdown
path: 'catalog/entity-facets'
params:
facet: 'kind'
# This selects the array element from the API fetch response. It finds the array with the name kind
# under the facets object
arraySelector: 'facets.kind'
# (Optional) This selects the field in the array to use for the value of each select item. If its not specified
# it will use the value of the item directly.
valueSelector: 'count'
# (Optional) This selects the field in the array to use for the label of each select item.
labelSelector: 'value'number
You can allow the user to enter a number using the number type:
parameters:
properties:
size:
type: numberobject
The object allows the collection of more complex types of data from the user. It contains the properties option to add variables to the object as follows:
parameters:
properties:
person:
type: object
properties:
name:
type: string
age:
type: numberYou may choose to make an object property to be mandatory using the required property.
parameters:
properties:
person:
type: object
required:
- name
properties:
name:
type: string
age:
type: numberarray
You can prompt for an array of properties using the array option. The items option can be any type: array, object, string or number as you like.
parameters:
properties:
languages:
type: array
items:
type: stringIf you would like to prompt the user to add entity tags, you can use the ui:field: EntityTagPicker as shown below.
parameters:
properties:
entityTags:
type: array
ui:field: EntityTagsPickerOutputs
Parameters can be retrieved later on by steps using parameter outputs. Here is an example of a parameter name being used by a debug:log step.
parameters:
properties:
name:
type: string
steps:
- id: log-message
name: Log Message
action: debug:log
input:
message: 'Hello, ${{ parameters.name }}!'If you need to reference elements of an array parameter you can refer to them using the following syntax:
steps:
- id: log-message
name: Log Message
action: debug:log
input:
message: 'Hello, ${{ parameters.names[0] }}!'An object parameter values can be reference in the way you might expect.
steps:
- id: log-message
name: Log Message
action: debug:log
input:
message: 'Hello, ${{ parameters.person.name }}!'Common Options
If you would like to default the value of a field you can use the default option:
parameters:
properties:
name:
type: string
default: 'world!'If you would like to prompt the users for a fixed list of options, you may use the enum option.
parameters:
properties:
size:
type: number
enum: [50, 100, 200]You can display a more human description to a field value by using title and description
parameters:
properties:
name:
type: string
title: 'Name'
description: 'Name to say hello to'Form Steps
It might be jarring for your user to enter a lot of parameters one after another on the same page, especially if some properties require validation. As such Backstage have provided form steps.
You can make use of form steps using the following example.
parameters:
- title: 'Fill in the Name'
properties:
name:
type: string
- title: 'Fill in the Age'
properties:
age:
type: numberPreviewing parameters
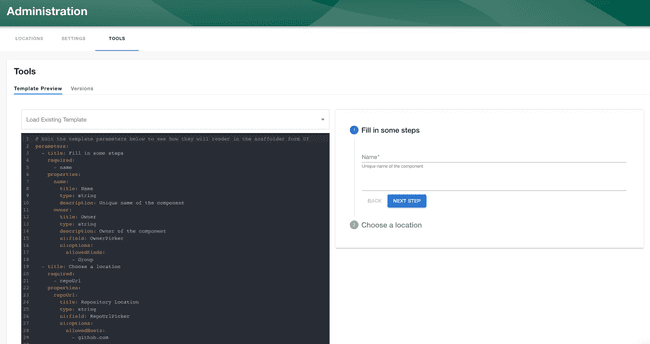
Template Preview, which is accessible via Tools > Template Preview provides a preview page for templates, where you can see a live preview of the template form. This is done in order to provide an easy way to preview scaffolder template form UIs without running your own local instance of the plugin or committing changes to the template.
More Reading
You can read more about parameter configuration in the official backstage docs here.
steps
Steps define the actions that are taken by the scaffolder template when it is run as a task. The scaffolder initially creates a temporary directory referred to as the workspace, in which files are downloaded, generated, updated and pushed to some external system. Each step that is defined is run in order.
Parameters taken from the user earlier may be used in the action steps using the syntax ${{ parameters.name }}.
Step Outputs
You can refer to the output of a previous step using the following syntax:
${{ steps["publish-step-id"].output.repoContentsUrl }}If the step id does not contain a special character you can also refer to it using the dot syntax.
${{ steps.publish.output.repoContentsUrl }}Parameter Values
You can refer to the value of a parameter using the following syntax:
${{ parameters["name"] }}If the parameter id does not contain a special character you can also refer to it using the dot syntax.
${{ parameters.name }}fetch:plain
Downloads content and places it in the workspace.
steps:
- action: fetch:plain
id: fetch-plain
name: Fetch plain
input:
url: ./plainOptionally, if you would prefer the data to be downloaded to a subdirectory in the workspace you may specify the ‘targetPath’ input option.
steps:
- action: fetch:plain
id: fetch-plain
name: Fetch plain
input:
url: ./plain
targetPath: fetched-dataOutputs
The fetch:plain action does not output any data.
fetch:template
This downloads a directory containing templated files. It then renders all the template variables into the files and directory names and content, and places the result in the workspace.
steps:
- action: fetch:template
id: fetch-template
name: Fetch template
input:
url: ./template
values:
name: ${{ parameters.name }}The templated files themselves can contain references to the values in the following way ${{ values.name }}. It uses the nunjucks templating language. More details can be found here.
i.e.
./template/README.md
# ${{ values.name }} service
This is a service Readme example. Please update me.Optionally, if you would prefer the data to be downloaded to a subdirectory in the workspace you may specify the ‘targetPath’ input option.
steps:
- action: fetch:template
id: fetch-template
name: Fetch template
input:
url: ./template
targetPath: fetched-data
values:
name: ${{ parameters.name }}You can also choose to not template specific files downloaded by the task by using the copyWithoutRender option. It may use file paths or globs.
steps:
- action: fetch:template
id: fetch-template
name: Fetch template
input:
url: ./template
copyWithoutRender:
- README.md
- src/**.ts
values:
name: ${{ parameters.name }}If you would like to limit the templating to very specific files, you can optionally add the .njk extension to the files and use the templateFileExtension option.
steps:
- action: fetch:template
id: fetch-template
name: Fetch template
input:
url: ./template
templateFileExtension: true
values:
name: ${{ parameters.name }}Outputs
The fetch:template action does not output any data.
publish:github
This action creates a new GitHub repository and publishes the files in the workspace directory to the repository. There is one mandatory parameter repoUrl. The repo url picker described in the string parameter description above.
The repoUrl must be in the format github.com?repo=<reponame>&owner=<owner org>
steps:
- action: publish:github
id: publish-repository
name: Publish Repository to Github
input:
repoUrl: 'github.com?repo=newreponame&owner=AcmeInc'By default it will create a repository with a master branch. If you prefer to use main you can do the following:
steps:
- action: publish:github
id: publish-repository
name: Publish Repository to Github
input:
repoUrl: 'github.com?repo=newreponame&owner=AcmeInc'
defaultBranch: mainThe access input parameter adds an admin collaborator to the repository. It can be a reference to a GitHub user or a team in GitHub.
steps:
- action: publish:github
id: publish-repository
name: Publish Repository to Github
input:
repoUrl: 'github.com?repo=newreponame&owner=AcmeInc'
access: AcmeInc/engineeringYou can protect the default branch from being pushed to directly by using protectDefaultBranch if your repository is part of a Github Pro account.
steps:
- action: publish:github
id: publish-repository
name: Publish Repository to Github
input:
repoUrl: 'github.com?repo=newreponame&owner=AcmeInc'
protectDefaultBranch: trueYou can enable code owner reviews using the requireCodeOwnerReviews option:
steps:
- action: publish:github
id: publish-repository
name: Publish Repository to Github
input:
repoUrl: 'github.com?repo=newreponame&owner=AcmeInc'
requireCodeOwnerReviews: trueThe repoVisibility option allows the repository to be made public. By default it will be a private repository.
steps:
- action: publish:github
id: publish-repository
name: Publish Repository to Github
input:
repoUrl: 'github.com?repo=newreponame&owner=AcmeInc'
repoVisibility: 'public'To cause merges to delete the source branch, you can enable the deleteBranchOnMerge setting.
steps:
- action: publish:github
id: publish-repository
name: Publish Repository to Github
input:
repoUrl: 'github.com?repo=newreponame&owner=AcmeInc'
deleteBranchOnMerge: trueIf you want to disable merge commits, squash merge and rebase merge you can do that with the settings allowMergeCommit, allowSquashMerge and allowRebaseMerge. By default, these are enabled.
steps:
- action: publish:github
id: publish-repository
name: Publish Repository to Github
input:
repoUrl: 'github.com?repo=newreponame&owner=AcmeInc'
allowMergeCommit: false
allowSquashMerge: false
allowRebaseMerge: falseBy default the repository will be populated with the files contained in the workspace directory. If you need to use a subdirectory, you can use the sourcePath option.
steps:
- action: publish:github
id: publish-repository
name: Publish Repository to Github
input:
repoUrl: 'github.com?repo=newreponame&owner=AcmeInc'
sourcePatch: './repoRoot'Collaborators can be added to the repository using the collaborators option. It takes an array of username or team and access. username is the GitHub username to allow collaboration.
The access option gives the user specific type of permissions. The options are pull, push, admin, maintain or triage. these equate to:
- pull (read)
- push (write)
- triage (triage)
- admin (admin)
- maintain (maintain - only for public repos)
The team value should be the Github team slug and should not include the org-name as a prefix.
steps:
- action: publish:github
id: publish-repository
name: Publish Repository to Github
input:
repoUrl: 'github.com?repo=newreponame&owner=AcmeInc'
collaborators:
- user: user1
access: admin
- team: github-team-name
access: pullThe topics allows adding topics to the created repository when its created.
steps:
- action: publish:github
id: publish-repository
name: Publish Repository to Github
input:
repoUrl: 'github.com?repo=newreponame&owner=AcmeInc'
topics:
- java
- rubyOutputs
The publish:github action produces two step outputs.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| remoteUrl | Url for the newly created repository |
| repoContentsUrl | Url that shows the contents of the repository |
These outputs can be retrieved by a subsequent step using:
steps:
- id: log-message
name: Log Message
action: debug:log
input:
message: 'RemoteURL: ${{ steps["publish-repository"].output.remoteUrl }}, ${{ steps["publish-repository"].output.repoContentsUrl }}!'publish:github:pull-request
This action creates a pull request against a pre-existing repository using the files contained in the workspace directory. The most basic example is:
steps:
- action: publish:github:pull-request
id: create-pull-request
name: Create a pull request
input:
repoUrl: 'github.com?repo=reponame&owner=AcmeInc'
branchName: ticketNumber-123
title: 'Make some changes to the files'
description: 'This pull request makes changes to the files in the reponame repository in the AcmeInc organization'If the updated code is contained in a subdirectory to the workspace directory, you can use the sourcePath to select it. If the files you want to target to update are in a subdirectory of the repository you can use the targetPath option.
steps:
- action: publish:github:pull-request
id: create-pull-request
name: Create a pull request
input:
repoUrl: 'github.com?repo=reponame&owner=AcmeInc'
branchName: ticketNumber-123
title: 'Make some changes to the files'
description: 'This pull request makes changes to the files in the reponame repository in the AcmeInc organization'
sourcePath: ./subdirectory
targetPath: ./subdirectoryYou can use the user that runs the scaffolder template to open the PR rather than opening it on behalf of the Roadie Github App by specifying the token field. The token can be injected by the RepoUrlPicker parameter as documented here
parameters:
- title: Choose a location
required:
- repoUrl
properties:
repoUrl:
title: Repository Location
type: string
ui:field: RepoUrlPicker
ui:options:
# Here's the option you can pass to the RepoUrlPicker
requestUserCredentials:
secretsKey: USER_OAUTH_TOKEN
additionalScopes:
github:
- workflow
allowedHosts:
- github.com
steps:
- action: publish:github:pull-request
id: create-pull-request
name: Create a pull request
input:
repoUrl: 'github.com?repo=reponame&owner=AcmeInc'
branchName: ticketNumber-123
title: 'Make some changes to the files'
description: 'This pull request makes changes to the files in the reponame repository in the AcmeInc organization'
# here's where the secret can be used
token: ${{ secrets.USER_OAUTH_TOKEN }}NB: The branch you use for the pull request must be a new branch for the repo.
Outputs
The publish:github:pull-request action produces two outputs.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| remoteUrl | Url to the new pull request |
| pullRequestNumber | Shows the number of the pull request |
They can be accessed in subsequent steps as follows:
steps:
- id: log-message
name: Log Message
action: debug:log
input:
message: 'RemoteURL: ${{ steps["create-pull-request.output.remoteUrl }}, ${{ steps["create-pull-request"].output.pullRequestNumber }}!'publish:bitbucket
This action creates a new Bitbucket repository and publishes the files in the workspace directory to the repository. There is one mandatory parameter repoUrl. The repo url picker described in the string parameter description above.
The repoUrl must be in the format bitbucket.org?repo=<project name>&workspace=<workspace name>&project=<project name>
steps:
- action: publish:bitbucket
id: publish-repository
name: Publish Repository to Bitbucket
input:
repoUrl: 'bitbucket.org?repo=newprojectname&workspace=workspacename&project=projectname'You can optionally add a description to the new repository.
steps:
- action: publish:bitbucket
id: publish-repository
name: Publish Repository to Bitbucket
input:
repoUrl: 'bitbucket.org?repo=newprojectname&workspace=workspacename&project=projectname'
description: 'My new project'By default the project will be created as a private repository. It can be made public using the repoVisibility option.
steps:
- action: publish:bitbucket
id: publish-repository
name: Publish Repository to Bitbucket
input:
repoUrl: 'bitbucket.org?repo=newprojectname&workspace=workspacename&project=projectname'
repoVisibility: 'public'By default the repository is created with a “master” branch. If you would like to use “main” instead you can us the defaultBranch option.
steps:
- action: publish:bitbucket
id: publish-repository
name: Publish Repository to Bitbucket
input:
repoUrl: 'bitbucket.org?repo=newprojectname&workspace=workspacename&project=projectname'
defaultBranch: 'main'By default the repository will be populated with the files contained in the workspace directory. If you need to use a subdirectory, you can use the sourcePath option.
steps:
- action: publish:bitbucket
id: publish-repository
name: Publish Repository to Bitbucket
input:
repoUrl: 'bitbucket.org?repo=newprojectname&workspace=workspacename&project=projectname'
sourcePatch: './repoRoot'Outputs
The publish:bitbucket action produces the following outputs.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| remoteUrl | Url for the newly created repository |
| repoContentsUrl | Url that shows the contents of the repository |
catalog:register
This action manually registers a component with the catalog.
You may want to do this if you haven’t configured autodiscovery of components or if you’re using a filename which doesn’t match your autodiscovery pattern.
It has two sets of options. The first allows you to configure the location as a complete url through catalogInfoUrl.
steps:
- action: catalog:register
id: register-with-catalog
name: Manually register with the catalog
input:
catalogInfoUrl: https://github.com/RoadieHQ/sample-service/blob/master/catalog-info-1.yaml
# optional: false # defaultThe second allows you to configure the repo containing the catalog file through repoContentsUrl and optionally a filepath through catalogInfoPath . You might use this along with the publish:github action.
steps:
- action: catalog:register
id: register-with-catalog
name: Manually register with the catalog
input:
repoContentsUrl: ${{ steps["publish-repository"].output.repoContentsUrl }}
# catalogInfoPath: catalog-info.yaml # default
# optional: false # defaultIn both cases you can pass an optional flag which determines if the location can be created before the catalog files exists.
catalog:write
This action creates a catalog-info.yaml file into the workspace directory. It takes an object that will be serialized as YAML into the body of the file.
steps:
- action: catalog:write
id: create-catalog-info-file
name: Create catalog file
input:
entity:
apiVersion: backstage.io/v1alpha1
kind: Component
metadata:
name: test
annotations: {}
spec:
type: service
lifecycle: production
owner: default/ownerIf you would like to create the catalog file in a custom location you can do that with the filePath option.
steps:
- action: catalog:write
id: create-catalog-info-file
name: Create catalog file
input:
filePath: '.backstage/catalog-info.yaml'
entity:
apiVersion: backstage.io/v1alpha1
kind: Component
metadata:
name: test
annotations: {}
spec:
type: service
lifecycle: production
owner: default/ownerOutputs
The catalog:write action does not have any outputs.
fs:delete
This action deletes items in the workspace. It has one input parameter files that can be provided an array of items to delete.
steps:
- action: fs:delete
id: delete-filds
name: Delete files
input:
files:
- files/deleteme
- otherfiletodeleteOutputs
The fs:delete action does not have any outputs.
fs:rename
This action allows you to move files within the workspace. The files option takes an array of objects containing from and to options.
steps:
- action: fs:rename
id: rename-files
name: Rename files
input:
files:
- from: copyfrom
to: copyto
- from: copyfrom1
to: copyto1Outputs
The fs:rename action does not have any outputs.
roadiehq:utils:fs:replace
This action replaces found string in files with content defined in input.
Required params:
- files: Collection of files and their replacing configuration. See structure of collection item below.
- files[].file: Path to the file to be modified
- files[].find: A text to be replaced
- files[].replaceWith: A text to be used to replace above
steps:
- id: Replace text in file
name: Replace
action: roadiehq:utils:fs:replace
input:
files:
- file: './file.1'
find: 'i_want_to_replace_this'
replaceWith: ${{ parameters.templated_text }}Outputs
The roadiehq:utils:fs:replace action does not have any outputs.
roadiehq:utils:fs:parse
Reads a file from the workspace and optionally parses it.
Params:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| path* | Path to the file to read. |
| parser | Optionally parse the content to an object. (yaml, json, multiyaml) |
spec:
owner: roadie
type: service
parameters:
- title: Path
properties:
path:
title: Path to the file
type: string
description: The path you want to get on your backstage instance
parser:
type: 'string'
enum: ['yaml', 'json', 'multiyaml']
steps:
- id: roadiehq-utils-fs-parse
name: backstage request
action: roadiehq:utils:fs:parse
input:
path: ${{ parameters.path }}
parser: ${{ parameters.parser }}Outputs
The roadiehq:utils:fs:parse action produces one output.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| content | Content of the file |
roadiehq:utils:serialize:yaml
Allows performing serialization on an object
Params:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| data* | Input data to perform serialization on. |
| replacer | Replacer array |
| options | YAML stringify options |
options:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| indent* | (default: 2) - indentation width to use (in spaces) |
| noArrayIndent | (default: false) - when true, will not add an indentation level to array elements |
| skipInvalid | (default: false) - do not throw on invalid types (like function in the safe schema) and skip pairs and single values with such types |
| flowLevel | (default: -1) - specifies level of nesting, when to switch from block to flow style for collections. -1 means block style everwhere |
| sortKeys | (default: false) - if true, sort keys when dumping YAML. If a function, use the function to sort the keys |
| lineWidth | (default: 80) - set max line width. Set -1 for unlimited width |
| noRefs | (default: false) - if true, don’t convert duplicate objects into references |
| noCompatMode | (default: false) - if true don’t try to be compatible with older yaml versions. Currently: don’t quote “yes”, “no” and so on, as required for YAML 1.1 |
| condenseFlow | (default: false) - if true flow sequences will be condensed, omitting the space between a, b. Eg. ‘[a,b]’, and omitting the space between key: value and quoting the key. Eg. ’{“a”:b}’ Can be useful when using yaml for pretty URL query params as spaces are %-encoded. |
| quotingType | (’ or ”, default: ’) - strings will be quoted using this quoting style. If you specify single quotes, double quotes will still be used for non-printable characters. |
| forceQuotes | (default: false) - if true, all non-key strings will be quoted even if they normally don’t need to. |
steps:
- id: roadiehq-utils-serialize-yaml
name: serialize yaml
action: roadiehq:utils:serialize:yaml
input:
data: { 'foo': 'bar' }
options:
noArrayIndent: trueOutputs
The roadiehq:utils:serialize:yaml action produces one output.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| serialized | Output result from serialization |
roadiehq:utils:serialize:json
Allows performing serialization on an object
Params:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| data* | Input data to perform serialization on. |
| replacer | Replacer array |
| space | Space character |
steps:
- id: roadiehq-utils-serialize-json
name: serialize json
action: roadiehq:utils:serialize:json
input:
data: { 'foo': 'bar' }
replacer:
- foo
- bar
space: '#'Outputs
The roadiehq:utils:serialize:json action produces one output.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| serialized | Output result from serialization |
roadiehq:utils:jsonata
Allows performing JSONata operations and transformations on input objects and produces the output result as a step output.
Params:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| data* | Input data to be transformed |
| expression* | JSONata expression to perform on the input |
steps:
- id: transform
name: Transform with jsonata
action: roadiehq:utils:jsonata
input:
data: foo
expression: <JSONata expression to perform on the input>Outputs
The roadiehq:utils:jsonata action produces one output.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| result | Output result from JSONata |
roadiehq:utils:jsonata:yaml:transform
Allows performing JSONata operations and transformations on a YAML file in the workspace. The result can be read from the result step output.
Params:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| path* | Input path to read yaml file |
| expression* | JSONata expression to perform on the input |
| options | YAML stringify options |
options:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| indent* | (default: 2) - indentation width to use (in spaces) |
| noArrayIndent | (default: false) - when true, will not add an indentation level to array elements |
| skipInvalid | (default: false) - do not throw on invalid types (like function in the safe schema) and skip pairs and single values with such types |
| flowLevel | (default: -1) - specifies level of nesting, when to switch from block to flow style for collections. -1 means block style everwhere |
| sortKeys | (default: false) - if true, sort keys when dumping YAML. If a function, use the function to sort the keys |
| lineWidth | (default: 80) - set max line width. Set -1 for unlimited width |
| noRefs | (default: false) - if true, don’t convert duplicate objects into references |
| noCompatMode | (default: false) - if true don’t try to be compatible with older yaml versions. Currently: don’t quote “yes”, “no” and so on, as required for YAML 1.1 |
| condenseFlow | (default: false) - if true flow sequences will be condensed, omitting the space between a, b. Eg. ‘[a,b]’, and omitting the space between key: value and quoting the key. Eg. ’{“a”:b}’ Can be useful when using yaml for pretty URL query params as spaces are %-encoded. |
| quotingType | (’ or ”, default: ’) - strings will be quoted using this quoting style. If you specify single quotes, double quotes will still be used for non-printable characters. |
| forceQuotes | (default: false) - if true, all non-key strings will be quoted even if they normally don’t need to. |
steps:
- id: transform
name: Transform YAML
action: roadiehq:utils:jsonata:yaml:transform
input:
path: a/b/test.txt
expression: <JSONata expression to perform on the input>
options:
noArrayIndent: trueOutputs
The roadiehq:utils:jsonata:yaml:transform action produces one output.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| result | Output result from JSONata yaml transform |
roadiehq:utils:jsonata:json:transform
Allows performing JSONata operations and transformations on a JSON file in the workspace. The result can be read from the result step output.
Params:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| path* | Input path to read yaml file |
| expression* | JSONata expression to perform on the input |
| replacer | Replacer array |
| space | Space character |
steps:
- id: transform
name: Transform JSON
action: roadiehq:utils:jsonata:json:transform
input:
path: a/b/test.txt
expression: <JSONata expression to perform on the input>
replacer:
- foo
- bar
space: '#'Outputs
The roadiehq:utils:jsonata:json:transform action produces one output.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| result | Output result from JSONata json transform |
json:merge
Merge new data into an existing JSON file.
Params:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| path* | Path to existing file to append. |
| content* | This will be merged into to the file. Can be either an object or a string. |
steps:
- id: merge
name: JSON merge
action: json:merge
input:
path: foo
content: barOutputs
The json:merge action produces one output.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| path | Path to the file that got appended to |
roadiehq:utils:json:merge
Merge new data into an existing JSON file.
Params:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| path* | Path to existing file to append. |
| content* | This will be merged into to the file. Can be either an object or a string. |
steps:
- id: merge
name: JSON merge
action: roadiehq:utils:json:merge
input:
path: foo
content: barOutputs
The roadiehq:utils:json:merge action produces one output.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| path | Path to the file that got appended to |
roadiehq:utils:merge
Merges data into an existing structured file.
Params:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| path* | Path to existing file to append. |
| content* | This will be merged into to the file. Can be either an object or a string. |
| options* | YAML stringify options (for YAML output only) |
options:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| indent* | (default: 2) - indentation width to use (in spaces) |
| noArrayIndent | (default: false) - when true, will not add an indentation level to array elements |
| skipInvalid | (default: false) - do not throw on invalid types (like function in the safe schema) and skip pairs and single values with such types |
| flowLevel | (default: -1) - specifies level of nesting, when to switch from block to flow style for collections. -1 means block style everwhere |
| sortKeys | (default: false) - if true, sort keys when dumping YAML. If a function, use the function to sort the keys |
| lineWidth | (default: 80) - set max line width. Set -1 for unlimited width |
| noRefs | (default: false) - if true, don’t convert duplicate objects into references |
| noCompatMode | (default: false) - if true don’t try to be compatible with older yaml versions. Currently: don’t quote “yes”, “no” and so on, as required for YAML 1.1 |
| condenseFlow | (default: false) - if true flow sequences will be condensed, omitting the space between a, b. Eg. ‘[a,b]’, and omitting the space between key: value and quoting the key. Eg. ’{“a”:b}’ Can be useful when using yaml for pretty URL query params as spaces are %-encoded. |
| quotingType | (’ or ”, default: ’) - strings will be quoted using this quoting style. If you specify single quotes, double quotes will still be used for non-printable characters. |
| forceQuotes | (default: false) - if true, all non-key strings will be quoted even if they normally don’t need to. |
steps:
- id: merge
name: JSON merge
action: roadiehq:utils:merge
input:
path: foo
content: bar
options:
noArrayIndent: trueOutputs
The roadiehq:utils:merge action produces one output.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| path | Path to the file that got appended to |
roadiehq:utils:fs:write
Creates a file with the content on the given path
Params:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| path* | Relative path to the file |
| content* | Content of the file |
steps:
- id: create
name: Create file
action: roadiehq:utils:fs:write
input:
path: foo
content: barOutputs
The roadiehq:utils:fs:write action produces one output.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| path | Path to the newly created file |
roadiehq:utils:zip
Zips the content of the path
Params:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| path* | Relative path to the file |
| outputPath* | The name of the result of the zip command |
steps:
- id: zip
name: Zip the workspace
action: roadiehq:utils:zip
input:
path: foo
outputPath: barOutputs
The roadiehq:utils:zip action produces one output.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| outputPath | Path to the newly created zip |
roadiehq:utils:fs:append
Append content to the end of the given file, it will create the file if it does not exist.
Params:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| path* | Path to existing file to append. |
| content* | This will be appended to the file |
steps:
- id: append
name: Append to file
action: roadiehq:utils:fs:append
input:
path: foo
content: barOutputs
The roadiehq:utils:fs:append action produces one output.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| path | Path to the file that got appended to |
fs:append
Appends text to a file within the workspace
Params:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| file* | The path of the file append to. This must be a path within the workspace. |
| text* | The text to append to the file. |
steps:
- id: append
name: Append to file
action: fs:append
input:
file: ${{ parameters.file }}
text: ${{ parameters.text }}Outputs
The fs:append action does not produce outputs.
fs:read
Reads a file from the workspace
Params:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| path* | Path to the file to read. |
steps:
- id: read
name: Reads a file
action: fs:read
input:
path: ${{ parameters.path }}Outputs
The fs:read action produces one output.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| content | Content of the file |
github:actions:dispatch
The github:actions:dispatch action allows you to trigger the execution of a GitHub action on a repository. The repoUrl option is a repo url for GitHub. The RepoUrlPicker documented above can generate this value. The workflowId can be the workflow id from the GitHub API or you can just use the filename for the workflow file itself. The branchOrTagName indicates which commit to run the workflow against.
This example will run the workflow defined in the “my-workflow-file.yaml” file on the “newreponame” repository on the “main” branch.
steps:
- action: github:actions:dispatch
id: trigger-build
name: Trigger Build
input:
repoUrl: 'github.com?repo=newreponame&owner=AcmeInc'
workflowId: 'my-workflow-file.yaml'
branchOrTagName: 'main'If the workflow takes additional inputs, you can pass these along with the workflowInputs option.
steps:
- action: github:actions:dispatch
id: trigger-build
name: Trigger Build
input:
repoUrl: 'github.com?repo=newreponame&owner=AcmeInc'
workflowId: 'my-workflow-file.yaml'
branchOrTagName: 'main'
workflowInputs:
parameter1: value1
parameter2: value2Outputs
The github:actions:dispatch action does not have any outputs.
github:webhook
You can configure a webhook on an existing repository in GitHub using this action. It takes repoUrl and webhookUrl. The repoUrl option needs to be in a GitHub repo format. The RepoUrlPicker documented above will generate a URL in the correct format.
steps:
- action: github:webhook
id: add-webhook
name: Add Webhook
input:
repoUrl: 'github.com?repo=newreponame&owner=AcmeInc'
webhookUrl: 'https://webhook-handler-service.abc/handle-webhook'You can configure a webhook secret using the webhookSecret option. You will likely want to provide this via an output from a previous step.
steps:
- action: github:webhook
id: add-webhook
name: Add Webhook
input:
repoUrl: 'github.com?repo=newreponame&owner=AcmeInc'
webhookUrl: 'https://webhook-handler-service.abc/handle-webhook'
webhookSecret: 'mysupersecretwebhooksecret'You can configure the types of events that trigger the webhook. For a full list of options see here
steps:
- action: github:webhook
id: add-webhook
name: Add Webhook
input:
repoUrl: 'github.com?repo=newreponame&owner=AcmeInc'
webhookUrl: 'https://webhook-handler-service.abc/handle-webhook'
events:
- push
- pull_requestIf you would like the webhook to receive every event, you can set the events to contain ”*“.
steps:
- action: github:webhook
id: add-webhook
name: Add Webhook
input:
repoUrl: 'github.com?repo=newreponame&owner=AcmeInc'
webhookUrl: 'https://webhook-handler-service.abc/handle-webhook'
events:
- '*'By default the payload of the webhook is form encoded, if you prefer json you can use contentType: json
steps:
- action: github:webhook
id: add-webhook
name: Add Webhook
input:
repoUrl: 'github.com?repo=newreponame&owner=AcmeInc'
webhookUrl: 'https://webhook-handler-service.abc/handle-webhook'
contentType: jsonYou can disable SSL on the webhook request using the insecureSsl option, but it is not advised.
steps:
- action: github:webhook
id: add-webhook
name: Add Webhook
input:
repoUrl: 'github.com?repo=newreponame&owner=AcmeInc'
webhookUrl: 'https://webhook-handler-service.abc/handle-webhook'
insecureSsl: trueOutputs
The github:webhook action does not have any outputs.
http:backstage:request
This action allows the Scaffolder task to run an HTTP request against the Backstage Backend API and handle the response. It can be useful for extending the scaffolder to call out to third party APIs. You can do this by configuring a proxy and then calling the proxy with this action.
The path should always point to a proxy entry with the following format: /proxy/<proxy-path>/<external-api-path> - i.e.: /proxy/snyk/org/<some-org>/projects or /proxy/circleci/api/projects (NB: the CircleCI proxy path is circleci/api/ but Snyk is just snyk/)
steps:
- action: http:backstage:request
id: http-request
name: Create a thing on the acme service
input:
method: GET
path: '/proxy/snyk/org/<some-org>/project/<some-project-id>'You can optionally add request params.
steps:
- action: http:backstage:request
id: http-request
name: Create a thing on the acme service
input:
method: POST
path: '/proxy/acme/thing'
params:
state: 'bar'The headers parameter allows setting headers on the request:
steps:
- action: http:backstage:request
id: http-request
name: Create a thing on the acme service
input:
method: GET
path: '/proxy/circleci/api/projects'
headers:
Accept: 'application/json'The body param allows you to set a request body. This is most likely going to be useful for POST requests.
steps:
- action: http:backstage:request
id: http-request
name: Create a thing on the acme service
input:
method: POST
path: '/api/proxy/acme/thing'
body: 'thingname=abc1'You can also have the action generate a json formatted body by setting a custom “Content-Type” header to “application/json” and then providing an object to the body param.
steps:
- action: http:backstage:request
id: http-request
name: Create a thing on the acme service
input:
method: POST
path: '/api/proxy/acme/thing'
headers:
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
body:
thingname: 'foo'Outputs
The http:backstage:request action has three outputs.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| code | Status code of the http response |
| headers | Dictionary containing all of the response headers and their values |
| body | Body of the response |
If there is a content-type header containing application/json the body param will contain the parsed object. Otherwise, it will contain an object with a single param message containing a string representing the body of the response.
debug:log
Use the debug:log action to print some information to the task console.
steps:
- action: debug:log
id: debug-log
name: Log Hello World
input:
message: 'Hello, World!'Outputs
The debug:log action does not have any outputs.
Conditional Steps
You can conditionally execute a scaffolder based on an input parameter.
steps:
- action: debug:log
id: debug-log
if: ${{ parameters.name }}
name: Log Hello World
input:
message: 'Hello, ${{ parameters.name }}!'Other Actions
You can find all the actions available to your Backstage instance by visiting the following page from within Backstage:
https://<tenant-name>.roadie.so/create/actions
Advanced
Calling an internal API
If you need a scaffolder step to contact a custom authenticated service or any public API for that matter that is not currently supported by a built-in action, you can do that using a combination of the http:backstage:request action and a backstage proxy configuration.
Start by creating a proxy configuration as described in this page
Then you can add a step to call that API using the http:backstage:request action as follows:
steps:
- action: http:backstage:request
id: http-request
name: Create a thing on the acme service
input:
method: POST
path: "/api/proxy/acme/thing"
- action: debug:log
id: log-result
name: Log the result of creating the thing
input:
message: "The response code was ${{ steps["http-request"].output.code }}'Escaping syntax
If you need to pass variable substitution syntax through without it being interpreted you can escape the syntax by wrapping it like so ${{ '${{ parameters.something }}' }}.
Creating re-usable snippets
You can inject in re-usable snippets of yaml into a template using the $yaml operator like so:
templates/debug-step.yaml
- name: Debug log 2
id: debug_log_2
action: 'debug:log'
input:
message: Second loglogging-template.yaml
apiVersion: scaffolder.backstage.io/v1beta3
kind: Template
metadata:
name: placeholder-example
title: Demonstrating the placeholder usage
description: Shows how to inject in a single re-usable step
spec:
owner: default/engineering
type: service
steps:
- name: Debug log 1
id: debug_log_1
action: 'debug:log'
input:
message: First log
$yaml: https://github.com/yourOrg/some-repo/blob/templates/debug-step.yamlNB: This can only be done for a single step as the re-usable section must be valid yaml.
Testing
Testing of templates is not well supported in Backstage currently, mostly due to the fact that many scaffolder actions perform side-effects.
A limited set of functionality exists to preview and edit parameters in a sandbox, and dry-run templates (skipping steps that perform mutations).
You can find these features at /create/edit.
It is also possible to test templates by changing the name and namespace of the template to indicate that it is a preview or test version, then adding it to the catalog via /register-existing-component using the version on a published feature branch.
This preview template will show up in the list of templates however so it is important to remove the entity after testing to avoid duplication, and also to make sure the title/description indicates that it is a temporary test.
Troubleshooting
Writing templates can be a little cumbersome at times. We have compiled a list of errors that we have seen in the past, that might help you determine the cause of your issue.
Template YAML input forms can also be tested at /tools using a live template preview viewer which speeds up the testing cycle.

Resource not accessible by integration
This error is referring to actions that interact GitHub. It means that the Roadie GitHub app is unable to read, create or update the resource/s that are being touched by the Scaffolder step.